shiro基础
Shiro入门学习
Apache Shiro是Java的一个安全(权限)框架
可以完成:认证、授权、加密、会话管理、与Web集成和缓存等
用户登录时把身份信息(用户名/手机号/邮箱地址等)和凭证信息(密码/证书等)封装成一个Token令牌,通过安全管理器中的认证器进行校验,成功则授权以访问系统
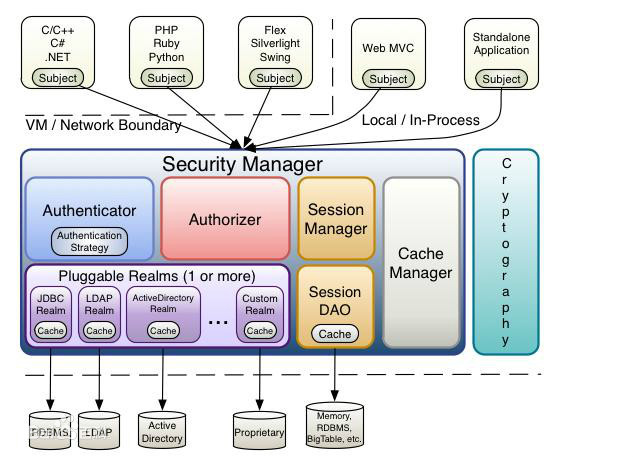
shiro三大功能模块
- Subject:主体,一般指用户。
- SecurityManager:安全管理器,管理所有Subject,可以配合内部安全组件。(类似于SpringMVC中的DispatcherServlet)
- Realms:用于进行权限信息的验证,一般需要自己实现。
一、默认Realm
shiro配置文件后缀为.ini(类似于.txt,但是支持复杂的数据格式,一般用于系统配置)
默认方法:通过ini配置文件(new IniRealm(“classpath:shiro.ini”)
public class Shiro1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建安全管理器对象
DefaultSecurityManager defaultSecurityManager = new DefaultSecurityManager();
//给安全管理器设置realm
defaultSecurityManager.setRealm(new IniRealm("classpath:shiro.ini"));
//给全局安全工具类securityUtils设置安全管理器
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(defaultSecurityManager);
//关键对象:subject主体
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//创建令牌
UsernamePasswordToken usernamePasswordToken = new UsernamePasswordToken("xiaochen","12s3");
try {
System.out.println("认证状态:" + subject.isAuthenticated());
subject.login(usernamePasswordToken);
System.out.println("认证状态:" + subject.isAuthenticated());
} catch (UnknownAccountException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("认证失败,用户名不存在");
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("认证失败,密码错误");
}
}
}
[users]
xiaochen=123
xiaowang=124
二、自定义Realm
AuthenticatingRealml类的doGetAuthenticationInfo方法用于认证realm
AuthorizingRealm类的doGetAuthorizationInfo方法用于授权realm
认证:
- 最终执行用户名比较: SimpleAccountRealm类中的doGetAuthenticationInfo方法
- 最终密码校验:AuthenticatingRealm类中的assertCredentialsMatch方法
自定义Realm实现认证
自定义Realm继承AuthorizingRealm(AuthorizingRealm继承了AuthenticatingRealm),实现doGetAuthenticationInfo和doGetAuthorizationInfo这两个抽象方法即可实现认证和授权处理
public class CustomerRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
// 授权
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
return null;
}
// 认证
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
// 在token中获取用户名
String principal = (String) authenticationToken.getPrincipal();
// 从数据库中获取用户名,此处直接模拟数据
if ("cyh".equals(principal)) {
// 参数一:数据库中的正确用户名, 参数二:数据库中的正确密码, 参数三:提供当前realm的名字 this.getName()
SimpleAuthenticationInfo simpleAuthenticationInfo = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal, "123", this.getName());
return simpleAuthenticationInfo;
}
return null;
}
}
public class CustomerRealmTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DefaultSecurityManager defaultSecurityManager = new DefaultSecurityManager();
CustomerRealm customerRealm = new CustomerRealm();
defaultSecurityManager.setRealm(customerRealm);
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(defaultSecurityManager);
UsernamePasswordToken usernamePasswordToken = new UsernamePasswordToken("cyh","123");
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
try {
subject.login(usernamePasswordToken);
System.out.println(subject.isAuthenticated());
} catch (AuthenticationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
三、Salt+MD5
MD5一般用来加密或者签名(校验和)
MD5算法不可逆,如果内容相同加密多少次结果都相同
MD5算法结果始终是一个16进制32位长度的字符串
为了解决被穷举破解密码的情况,我们一般对用户输入的密码进行“加盐”以增加密码复杂性,提高安全性。
所谓加盐即随机生成一段字符对用户输入的密码进行包装(按照一定的规则将盐拼接到原密码),随后再进行MD5加密存储到数据库中,同时也要把盐值进行存储,这样首先提高密码复杂性难以被穷举破解,其次即使被破解了拿到盐值后也难以推算出盐是如何拼接在原密码中。
public class Md5Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 第一个参数为待加密值,第二个参数为盐值(默认加在待加密值前面),第三个参数为hash散列次数(默认1次)
Md5Hash md5Hash = new Md5Hash("123");
System.out.println(md5Hash.toHex()); // 202cb962ac59075b964b07152d234b70
Md5Hash md5Hash1 = new Md5Hash("123", "o12*k");
System.out.println(md5Hash1.toHex()); // 1fb300cc9a77b971ab845263d802966b
Md5Hash md5Hash2 = new Md5Hash("123","o12*k",1024);
System.out.println(md5Hash2.toHex()); // a72061f5b311794e5068574ece5935be
}
}
public class CustomerMd5Realm extends AuthorizingRealm {
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
return null;
}
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
String principal = (String) authenticationToken.getPrincipal();
if ("cyh".equals(principal)) {
// 参数一:数据库用户名,参数二:数据库md5+salt加密散列后的密码,参数三:注册时的盐,参数四:realm的名字
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal, "a72061f5b311794e5068574ece5935be", ByteSource.Util.bytes("o12*k"), this.getName());
}
return null;
}
}
public class CustomerMd5RealmTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DefaultSecurityManager defaultSecurityManager = new DefaultSecurityManager();
CustomerMd5Realm customerMd5Realm = new CustomerMd5Realm();
// 获取密码匹配器(默认使用equals匹配)
HashedCredentialsMatcher hashedCredentialsMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher();
// 选择使用的加密算法
hashedCredentialsMatcher.setHashAlgorithmName("md5");
// 设置hash散列次数
hashedCredentialsMatcher.setHashIterations(1024);
// 设置realm使用hash凭证匹配器
customerMd5Realm.setCredentialsMatcher(hashedCredentialsMatcher);
defaultSecurityManager.setRealm(customerMd5Realm);
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(defaultSecurityManager);
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("cyh","123");
try {
subject.login(token);
System.out.println("登录成功");
} catch (UnknownAccountException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("认证失败,用户名不存在");
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("认证失败,密码错误");
}
}
}
四、授权
授权,即访问控制,控制谁能访问哪些资源。主体进行身份认证后需要分配权限方可访问系统的资源,对于某些资源没有权限是无法访问的。
-
基于角色的访问控制权限:以角色为中心
-
if(subject.hasRole("admin")){ //操作什么资源 }
-
-
基于资源的访问控制权限:以资源为中心
-
if(subject.isPermitted("user:create:*")){ //对用户模块的所有实例具有创建权限 } if(subject.isPermitted("user:*:01")){ //对用户模块的01号资源具有所有权限 }
-
-
权限字符串:
资源标识符:操作:资源实例标识符,意思是对哪个资源的哪个实例具有什么操作权限(*代表通配)
if (subject.isAuthenticated()) {
System.out.println(subject.hasRole("admin"));
System.out.println(subject.hasRole("users"));
System.out.println(subject.isPermitted("user:create:*"));
System.out.println(subject.isPermitted("product:create:01"));
}
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
String primaryPrincipal = (String) principalCollection.getPrimaryPrincipal();//获得用户名
System.out.println("身份信息:" + primaryPrincipal);
// 根据身份信息 用户名 获取当前用户的角色信息,权限信息
SimpleAuthorizationInfo simpleAuthorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
// 将数据库中查询到的角色信息赋值给权限对象
simpleAuthorizationInfo.addRole("users");
// 将数据库中查询到的权限信息赋值给权限对象
simpleAuthorizationInfo.addStringPermission("users:update:01");
simpleAuthorizationInfo.addStringPermission("product:create");
return simpleAuthorizationInfo;
}
授权方式
- 编程式(如下注释处)
- 注解式(@RequireRoles(""))
- 标签式(应用于JSP中)
@RequestMapping("save")
@RequiresRoles(value = {"admin","user"}, logical = Logical.OR)
//@RequiresPermissions("user:update:*")
public String save(){
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
// if (subject.hasRole("admin")) {
// System.out.println("保存订单");
// }
// else {
// System.out.println("无权访问");
// }
// if (subject.isPermitted("user:save:01")) {
// System.out.println("保存订单");
// }
// else {
// System.out.println("无权访问");
// }
return "redirect:/index.html";
}
五、SpringBoot整合Shiro
Maven
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0</version>
</dependency>
自定义CustomerRealm
public class CustomerRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
String primaryPrincipal = (String) principalCollection.getPrimaryPrincipal();
User user = userService.findRolesByUsername(primaryPrincipal);
SimpleAuthorizationInfo simpleAuthorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
List<Role> roles = user.getRoles();
roles.forEach(role -> {
simpleAuthorizationInfo.addRole(role.getName());
List<Permission> permissions = userService.findPermissionsByRoleId(role.getId());
permissions.forEach(permission -> simpleAuthorizationInfo.addStringPermission(permission.getName()));
});
return simpleAuthorizationInfo;
}
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
String principal = (String) authenticationToken.getPrincipal();
User user = userService.findByUsername(principal);
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(user)) {
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user.getUsername(),user.getPassword(), ByteSource.Util.bytes(user.getSalt()),this.getName());
}
return null;
}
}
ShiroConfig
@Configuration
public class ShiroConfig {
// 创建ShiroFilter,负责拦截所有请求
@Bean
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilterFactoryBean(DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager){
ShiroFilterFactoryBean shiroFilterFactoryBean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
// 给filter设置安全管理器
shiroFilterFactoryBean.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager);
// 配置系统受限资源
// 配置系统公共资源
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<String,String>();
map.put("/index.html","authc"); // authc表示请求这个资源需要认证和授权,未授权会自动跳转至认证界面
map.put("/order/save","authc");
// /**通配符表示所有资源受限,需要先将登录设置为公共资源再设置通配受限
// 相应的还有anon过滤器,指定的资源可以匿名访问
// 设置认证界面路径
shiroFilterFactoryBean.setLoginUrl("/login.html"); // 默认认证界面路径为login.jsp
shiroFilterFactoryBean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(map);
return shiroFilterFactoryBean;
}
// 创建安全管理器
@Bean
public DefaultWebSecurityManager getDefaultWebSecurityManager(@Qualifier("getRealm") Realm realm){
DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
// 给安全管理器设置realm
defaultWebSecurityManager.setRealm(realm);
return defaultWebSecurityManager;
}
// 创建自定义Realm
@Bean
public CustomerRealm getRealm(){
CustomerRealm customerRealm = new CustomerRealm();
HashedCredentialsMatcher hashedCredentialsMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher();
hashedCredentialsMatcher.setHashAlgorithmName("md5");
hashedCredentialsMatcher.setHashIterations(1024);
customerRealm.setCredentialsMatcher(hashedCredentialsMatcher);
return customerRealm;
}
}
Utils
public class SaltUtils {
public static String getSalt(int len){
String list = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz1234567890[];,./!@#$%^&*()_+-=";
String result = "";
for(int i=0; i<len; i++){
result += list.charAt(new Random().nextInt(list.length()));
}
return result;
}
}
页面
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
首页
<ul>
<li >保存订单</li>
</ul>
<a href="/shiro/user/logout">退出</a>
</body>
</html>
register.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="http://localhost:8889/shiro/user/register" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"> <br>
密码:<input type="text" name="password"> <br>
<input type="submit" value="注册">
</form>
</body>
</html>
login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="http://localhost:8889/shiro/user/login" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"> <br>
密码:<input type="text" name="password"> <br>
<input type="submit" value="登录">
</form>
</body>
</html>
controller
UserController
@Controller
@RequestMapping("user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@PostMapping("login")
public String login(String username, String password){
//获取主体(ShiroConfig中创建了安全管理器,则SecurityUtils会自动配置上安全管理器)
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
try {
subject.login(new UsernamePasswordToken(username,password));
return "redirect:/index.html";
} catch (AuthenticationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return "redirect:/login.html";
}
}
@GetMapping("logout")
public String logout(){
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
subject.logout();
return "redirect:/login.html";
}
@PostMapping("register")
public String register(User user) {
userService.register(user);
return "redirect:/login.html";
}
}
OrderController
@Controller
@RequestMapping("order")
public class OrderController {
@RequestMapping("save")
@RequiresRoles(value = {"admin","user"}, logical = Logical.OR)
@RequiresPermissions("user:update:*")
public String save(){
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
// if (subject.hasRole("admin")) {
// System.out.println("保存订单");
// }
// else {
// System.out.println("无权访问");
// }
// if (subject.isPermitted("user:save:01")) {
// System.out.println("保存订单");
// }
// else {
// System.out.println("无权访问");
// }
return "redirect:/index.html";
}
}
serviceimpl
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
@Override
public void register(User user) {
user.setId(2L);
String salt = SaltUtils.getSalt(8);
user.setSalt(salt);
Md5Hash md5Hash = new Md5Hash(user.getPassword(), salt, 1024);
user.setPassword(md5Hash.toHex());
userDao.save(user);
}
@Override
public User findByUsername(String username) {
return userDao.findByUsername(username);
}
@Override
public User findRolesByUsername(String username) {
return userDao.findRolesByUsername(username);
}
@Override
public List<Permission> findPermissionsByRoleId(Long id) {
return userDao.findPermissionsByRoleId(id);
}
}
dao
@Mapper
public interface UserDao {
void save(User user);
User findByUsername(String username);
User findRolesByUsername(String username);
List<Permission> findPermissionsByRoleId(Long id);
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="cn.ken.springboot_shiro.dao.UserDao">
<insert id="save" parameterType="user">
insert into user values(#{id},#{username},#{password},#{salt})
</insert>
<select id="findByUsername" parameterType="string" resultType="user">
select * from user where username = #{username}
</select>
<resultMap id="userMap" type="User">
<id column="uid" property="id"/>
<result column="username" property="username"/>
<collection property="roles" javaType="list" ofType="role">
<id column="rid" property="id"/>
<result column="rname" property="name"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findRolesByUsername" parameterType="String" resultMap="userMap">
SELECT u.id uid, u.username, r.id rid, r.name rname
FROM `user` u LEFT JOIN `user_role` ur
ON u.id = ur.user_id
LEFT JOIN `role` r
ON ur.role_id = r.id
WHERE u.username = #{username}
</select>
<select id="findPermissionsByRoleId" parameterType="Long" resultType="permission">
SELECT p.id, p.name, p.url FROM `role` r
LEFT JOIN `role_permission` rp
ON r.id = rp.role_id
LEFT JOIN `permission` p
ON p.id = rp.per_id
WHERE r.id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
entity
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class User implements Serializable {
private Long id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String salt;
private List<Role> roles;
}
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Role implements Serializable {
private Long id;
private String name;
private List<Permission> permissions;
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Permission implements Serializable {
private Long id;
private String name;
private String url;
}
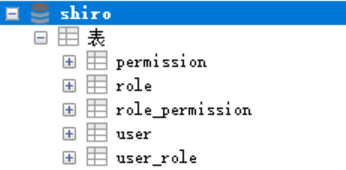
数据表
六、缓存
以上操作存在一定的问题,就是需要频繁的操作数据库,对数据库压力过大,故引入缓存
EhCache(程序内部缓存,重启数据丢失)
1、引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId>
<artifactId>shiro-ehcache</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0</version>
</dependency>
2、开启缓存
在ShiroConfig的getRealm中设置
// 创建自定义Realm
@Bean
public CustomerRealm getRealm(){
CustomerRealm customerRealm = new CustomerRealm();
HashedCredentialsMatcher hashedCredentialsMatcher = new HashedCredentialsMatcher();
hashedCredentialsMatcher.setHashAlgorithmName("md5");
hashedCredentialsMatcher.setHashIterations(1024);
customerRealm.setCredentialsMatcher(hashedCredentialsMatcher);
// 开启缓存管理
customerRealm.setCacheManager(new EhCacheManager());
customerRealm.setCachingEnabled(true); // 开启全局缓存
customerRealm.setAuthenticationCachingEnabled(true); // 开启认证缓存
customerRealm.setAuthenticationCacheName("authenticationCache");
customerRealm.setAuthorizationCachingEnabled(true); // 开启授权缓存
customerRealm.setAuthorizationCacheName("authorizationCache");
return customerRealm;
}
3、启动刷新页面进行测试
如果控制台没有任何sql展示说明缓存已经开启